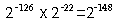 to
to
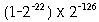 inclusive.
inclusive.
|
|
A number is denormalized if the exponent field contains all 0's and the fraction field does not contain all 0's.
Thus denormalized single-precision numbers can be in the range (plus
or minus)
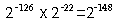 to
to
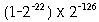 inclusive.
inclusive.
Denormalized double-precision numbers can be in the range (plus
or minus)
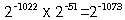 to
to
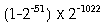 inclusive.
inclusive.
Denormalized extended-precision numbers do not have a 1 bit in
position 63. Therefore, it stores numbers in the range (plus
or minus)
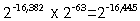 to
to
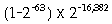 inclusive.
inclusive.
Both positive and negative zero values exist, but they are treated the same during floating point calculations.